ACT Question for April 19th
Pyroclastic flows are mixtures of hot gases and ash that travel down the sides of a volcano. Once a flow's forward motion stops, the ash settles and a flow deposit is formed. Three studies were done to simulate pyroclastic flows and flow deposits.
A funnel was positioned at the top of an 80 cm x 200 cm inclined plane. Glass beads with diameters between 425 micrometers (μm) and 600 μm were glued at an even density over the entire upper surface to decrease the smoothness of the inclined plane. The diameter of the funnel opening could be varied as could the angle of the inclined plane. A quantity of microbeads (glass beads with a density of 2.5 g/cm3 and diameters between 300 μm and 400 μm) was placed in the funnel. When released from the funnel, the microbeads flowed down the incline and formed a flow deposit (see diagram).
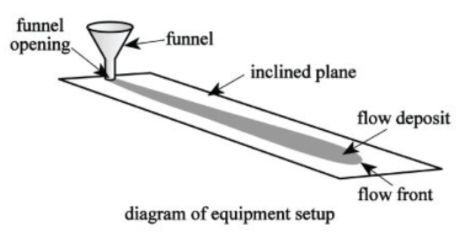
In each trial, microbeads were released from the funnel at a different flux (rate of release from the funnel opening).
Based on the description of the equipment used in the studies, the flux of microbeads was most likely increased by doing which of the following?