When water droplets containing dissolved ions freeze, opposite charges may develop between the newly formed ice crystals and the still unfrozen droplets. As the ice crystals and droplets separate in a cloud, charged regions form.
Solutions of four sodium (Na) salts, containing fluoride (F-), chloride (Cl-), bromide (Br-), and iodide (I-) ions, were each made at six different concentrations, in moles per liter (moles/L). The solutions were slowly cooled until freezing began. The electrical potential (whether the droplets had a positive or negative charge with respect to the ice crystals) was measured in volts. The results are shown in the Figure.
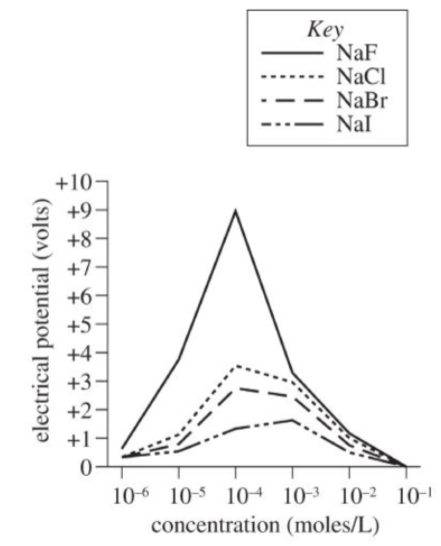
A scientist could best determine which ion (F-, Cl-, Br-, or I-) produced the greatest electrical potential in the Experiment by comparing the electrical potential that develops between ice and:
Correct
Incorrect
The correct answer is (A).
Getting to the Answer: The experiment measured the electrical potential (the charge with respect to ice crystals) for solutions each containing either F-, Cl-, Br-, or I- at different concentrations. To determine which ion produced the greatest electrical potential, other variables need to be held constant. Evaluate each answer choice to determine which setup varies only the ion type.
(A) Correct: the effect of ion type on electrical potential could be determined if the other independent variable in the Experiment, ion concentration, was held constant
(B) Incorrect: comparing electrical potential of a single sodium salt solution at different concentrations would give the effects of varying concentration for that particular ion, not the effects of varying ion type
(C) Incorrect: comparing electrical potential of a single sodium salt solution at different concentrations would give the effects of varying concentration for that particular ion, not the effects of varying temperature
